中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (23): 3691-3695.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.23.014
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
山羊神经干细胞的分离培养及体外诱导分化
夏许可,张 伟,余杰锋,章 莹
- 1解放军广州军区广州总医院骨科医院,广东省广州市 510010;2南方医科大学研究生院 广东省广州市 510515;3广东冠昊生物科技股份有限公司,广东省广州市 510530;4广州医科大学研究生院,广东省广州市 510182
In vitro culture and differentiationof goat neural stem cells
Xia Xu-ke1, 2, Zhang Wei3, Yu Jie-feng1, 4, Zhang Ying1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; 2Graduate School of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 3Grandhope Biotech Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; 4Graduate School of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510182, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
背景:文献报道不同种类的神经调控因子及神经胶质细胞对神经干细胞分化成熟具有不同的作用,但大动物的神经干细胞培养报道则相对较少。
目的:探究山羊神经干细胞的培养条件及体外诱导分化结果。
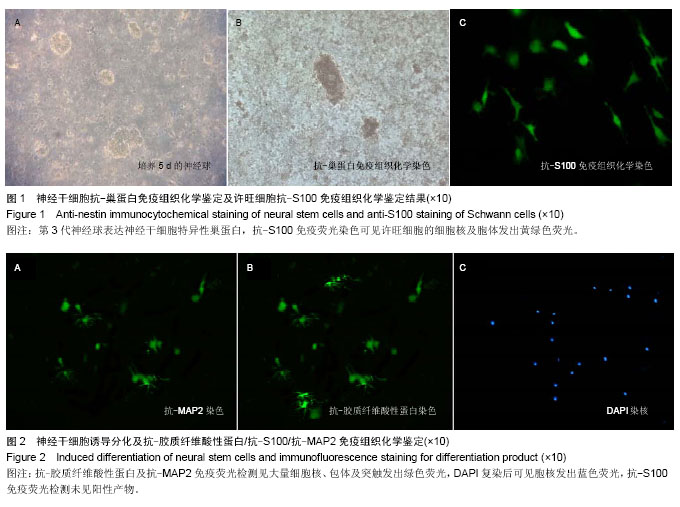
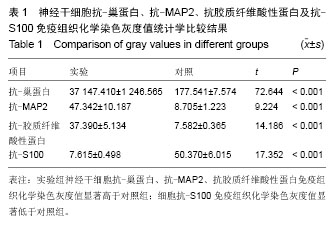
方法:取幼羊脑组织分离神经干细胞后于神经干细胞全培养液中悬浮培养,后期行抗-巢蛋白一抗免疫组织化学染色鉴定,同时取坐骨神经分离培养许旺细胞;以血清诱导干细胞体外诱导分化后行抗-S100一抗、抗-胶质纤维酸性蛋白一抗、抗-MAP2一抗染色分别标记许旺细胞及神经胶质细胞,以未添加一抗做对照,计算图像灰度值与对照组进行统计学比较。
结果与结论:成功分离培养抗-巢蛋白染色阳性神经球及抗-S100染色阳性许旺细胞,后期神经干细胞体外诱导分化得抗-胶质纤维酸性蛋白、抗-MAP2染色阳性细胞,其免疫组织化学染色灰度值显著高于对照组;分化产物抗-S100染色为阴性,其免疫组织化学染色灰度值显著低于对照组。结果表明山羊神经干细胞可经体外诱导分化为神经元及星形胶质细胞,未发现神经干细胞诱导分化为许旺细胞。
中图分类号:
.jpg)